Unit 2: Thermodynamics
Concepts
Ideal gas: a theoretical gas that follows the ideal gas law. Qualities of an ideal gas include:
- There is a very large number of particles, all with the same mass m. They all move randomly at different speeds in straight line paths.
- The relative size of each particle is extremely small compared to the container they are in. On average, each particle is relatively very far from others.
- The particles are assumed to exert no molecular forces on each other other than collisions.
- All collisions between particles, including each particle and the walls of the container, are assumed to be elastic. Perfect elasticity means that no energy is lost.
Laws of thermodynamics - The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy equals the heat added to the gas plus the work done on the system/gas. The second law states that heat can flow spontaneously from a hot to a cold object, but not from a cold to hot object.
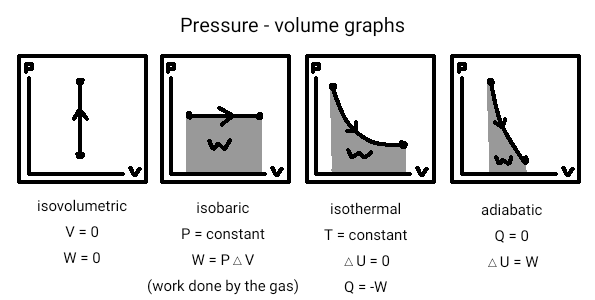
Thermodynamic processes - 4 processes that gases can be taken through. These processes are:
- Isothermal - where the temperature of the gas is kept constant.
- Isoberic - where the pressure of the gas is kept constant.
- Isovolumetric - where the volume of the gas is kept constant.
- Adiabatic - where the temperature changes but heat isn't added or removed. This is done by making the process fast enough that there's no time for heat to be added or removed from the surroundings.
Heat - the energy transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature. Can be measured in multiple units including joules, calories, kilocalories, British thermal units (BTU), and therms (105 BTU).
Heat transfer - How heat is transferred between systems. The 3 methods of heat transfer are:
- Conduction - can occur in solids, liquids, and gases. Happens through molecular collisions.
- Convection - usually only occurs in liquids and gases. Happens through a bulk of molecules moving from one place to another.
- Radiation - the only method that can happen through empty space, thanks to electromagnetic waves.
Phase transition - The change from one state of matter (solid, liquid, or gas) to another. The temperature of a substance will not change until all of the substance has transitioned as long as the system is in equilibrium.
Entropy - Can be thought of as the amount of disorder in a system. Also represents the amount of energy in a system that's unusable for work. The total entropy of a system and its environment will always increase as a result of any natural process.
Boltzmann's constant - (1.38 x 10-23 J/k).
Formulas
PV = nRT - The ideal gas law. (Pressure)(volume) = (number of moles)(universal gas constant)(temperature of gas).
△U = Q + W - The 1st law of thermodynamics as a formula. The change in internal energy = heat added to the gas + work done to the gas.
F = PA - The force that a gas exerts on a surface. (Force of gas) = (pressure)(surface area).
Average KE = (3/2)KbT - Formula used to find the average kinetic energy of particles in an ideal gas. (Average kinetic energy) = (3/2)(Boltzman's constant)(temperature of gas).
Vrms = √((3KbT)/m) - Formula used to find the root mean square velocity of an individual molecule in an ideal gas. (Root mean square velocity) = √(((3)(Boltzmann's constant)(temperature of the gas))/(molecular mass)).
(Q/△t) = kA(△T/L) - Formula used for thermal conduction. ((Heat)/(Change of time)) = (thermal conductivity)(surface area)((change in temperature)/(length of material where heat is being transferred)).
U = (3/2)nRT - Used to find the internal energy of a gas. Internal energy = (3/2)(number of moles)(universal gas constant)(temperature of the gas).